Reading and Understanding a GIA Diamond Certificate
A Complete Guide for Those Who Want to Buy Diamond
When you decide to buy diamond, understanding the diamond’s quality is crucial to making an informed decision. One of the most reliable ways to assess a diamond’s attributes is through its certification, particularly the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) Diamond Certificate. The GIA certificate is widely regarded as the gold standard in the diamond industry, providing detailed insights into a diamond’s characteristics. By reading and understanding this certificate, you can ensure that you’re purchasing a high-quality diamond and getting good value for your money.
In this guide, we will break down how to read and understand a GIA Diamond Certificate, and explain why this certification is essential when you buy diamond.
What is a GIA Diamond Certificate?
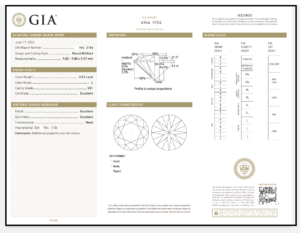
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) is a globally respected nonprofit organization that provides unbiased and reliable grading of diamonds. A GIA Diamond Certificate, also known as a GIA Diamond Grading Report, is a detailed document that describes a diamond’s physical and aesthetic properties. It includes an in-depth analysis of the diamond’s cut, color, clarity, and carat weight — collectively known as the Four Cs — as well as additional characteristics that can affect its appearance and value.
The GIA certificate provides important information that can help you when you buy diamond, giving you the assurance that your purchase is authentic and of high quality.
Key Sections of a GIA Diamond Certificate
A GIA Diamond Certificate is a thorough document that covers a range of characteristics about the diamond. Here’s a breakdown of the key sections to look for:
1. Report Summary
The Report Summary section is a concise overview of the most crucial aspects of the diamond. This includes:
- Shape and Cutting Style: The shape refers to the overall form of the diamond (round, oval, cushion, princess, etc.), while the cutting style refers to how the diamond is faceted (e.g., round brilliant, step cut). These two factors significantly affect how a diamond reflects light.
- Carat Weight: This indicates the size of the diamond. A carat is equivalent to 200 milligrams, and this measurement is one of the key indicators of a diamond’s value.
- Measurements: In addition to carat weight, the dimensions of the diamond, including length, width, and depth, are noted.
- Clarity: This section explains the diamond’s clarity grade, based on the presence or absence of internal flaws (inclusions) and external imperfections (blemishes).
- Color: This defines the diamond’s color grade, ranging from colorless (D) to light yellow or brown (Z). Diamonds with less color are considered more valuable.
2. The Four Cs of Diamond Grading
The Four Cs are the most important factors used to determine the quality and value of a diamond. When you buy diamond, these are the attributes you need to pay attention to:
Cut
The cut is arguably the most important factor in a diamond’s visual appeal. A well-cut diamond will display brilliance and sparkle, while a poorly cut one will appear dull. The GIA uses a grading scale for cut that ranges from Excellent to Poor, evaluating factors like symmetry, proportions, and polish. The cut has a significant impact on the overall appearance of the diamond, even more so than color or clarity.
Color
Diamonds come in a range of colors, from completely colorless to shades of yellow or brown. GIA grades diamonds on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). Colorless diamonds are the most valuable, and the less color a diamond has, the rarer and more expensive it is. When you buy diamond, consider how the color grade aligns with your preferences and budget.
Clarity
Clarity refers to the presence of internal or external imperfections in the diamond, known as inclusions and blemishes. The GIA uses a scale that ranges from Flawless (no inclusions or blemishes visible under 10x magnification) to Included (inclusions or blemishes that are easily visible to the naked eye). The fewer inclusions or blemishes, the more valuable the diamond is.
Carat Weight
Carat weight is a measure of a diamond’s size. One carat is equivalent to 200 milligrams. When you buy diamond, remember that while carat weight affects the price, it’s not the only factor to consider. A larger diamond with lower cut, clarity, or color grades may not be as valuable as a smaller but higher-quality diamond.
3. Additional Features
In addition to the Four Cs, a GIA Diamond Certificate may contain other important details:
Fluorescence
Fluorescence refers to the diamond’s ability to emit visible light (usually blue) when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. While fluorescence isn’t always noticeable, it can impact a diamond’s value and appearance. Diamonds with strong fluorescence might appear hazy or milky in certain lighting conditions, while diamonds with little to no fluorescence are typically preferred.
Symmetry and Polish
Symmetry refers to how well the diamond’s facets are aligned, while polish refers to the quality of the diamond’s surface. A diamond with excellent symmetry and polish will reflect light more efficiently, enhancing its brilliance. Both symmetry and polish are graded on a scale from Excellent to Poor.
4. The Plot Diagram
The plot diagram is one of the most important sections of the GIA Diamond Certificate. This detailed illustration shows the diamond’s inclusions and blemishes as seen under magnification. The plot helps to identify the specific characteristics of the diamond, ensuring it matches the certificate. It’s particularly useful if you are buying diamonds from a retailer or considering reselling or insuring your diamond later.
5. Laser Inscription
Some diamonds are laser-inscribed with a unique identification number along the girdle (the edge of the diamond). This inscription is tiny, but it links the diamond to its GIA certificate and ensures that the diamond can be traced back to its certification in case of loss or theft.
6. Comments Section
The comments section provides additional details about the diamond that might not fit into the main grading categories. This could include special remarks about the diamond’s appearance, such as descriptions of unique inclusions or features that might affect its visual appeal or value.
How to Read the GIA Certificate When You Want to Buy Diamond
When you’re ready to buy diamond, carefully reviewing the GIA certificate will give you the information needed to make an informed decision. Here’s how to effectively read the GIA certificate:
1. Focus on the Four Cs
Start by looking at the Four Cs: Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat Weight. These are the most important indicators of a diamond’s value and appearance. Depending on your preferences and budget, prioritize the characteristics that matter most to you. For instance, if you value brilliance above all, focus on the cut. If you’re looking for a diamond with minimal visible color or flaws, pay attention to color and clarity.
2. Understand the Cut Grade
The cut grade is crucial because it affects how the diamond reflects light. A high-quality cut will make the diamond sparkle more, which is often more noticeable than color or clarity. When you buy diamond, always check the cut grade, as it can drastically impact the diamond’s overall appearance.
3. Consider Fluorescence and Symmetry
If the diamond has strong fluorescence, it may affect its visual appearance under UV light. You should also check the symmetry and polish grades, as these factors influence how well the diamond reflects light.
4. Refer to the Plot Diagram
The plot diagram is an essential tool for understanding the diamond’s inclusions and blemishes. It can help confirm the diamond’s identity and ensure that it matches the description on the certificate.
5. Check for Laser Inscription
If the diamond has a laser inscription, make sure the identification number matches what is listed on the certificate. This serves as a permanent and traceable identifier for your diamond.
Conclusion
A GIA Diamond Certificate is a valuable resource when you buy diamond, offering in-depth details about a diamond’s quality and authenticity. By understanding how to read and interpret this certificate, you ensure that you are purchasing a diamond that meets your expectations for both beauty and value. Whether you’re buying a diamond for an engagement ring, a special gift, or as an investment, the GIA certificate offers peace of mind that your diamond has been thoroughly evaluated by experts. So, the next time you decide to buy diamond, take the time to review the GIA certificate carefully to make an informed and confident purchase.